PG S3 M. Sc. AI First internal examination, Machine Learning, September 2024
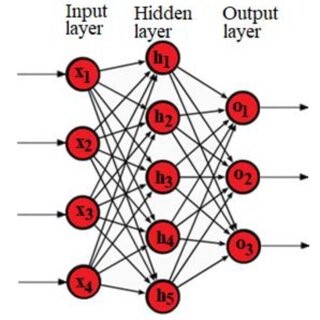
Solutions – Machine Learning Section A 1. Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) is an optimization algorithm used for training machine learning models, particularly neural networks. It is a variant of gradient descent that updates model parameters using only a single data point (or a small batch) at a time. 2. MTL can be useful in many applications such as natural language processing, computer vision, and healthcare, where multiple tasks are related or have some commonalities. It is also useful when the data is limited, MTL can help to improve the generalization performance of the model by leveraging the information shared across tasks. 3. A regularized problem incorporates a regularization term into the objective function to prevent overfitting and improve model generalization. Regularization adds a penalty to the loss function based on the complexity of the model parameters. n under-constrained problem occurs when t...